Request a Demo of Tessian Today.
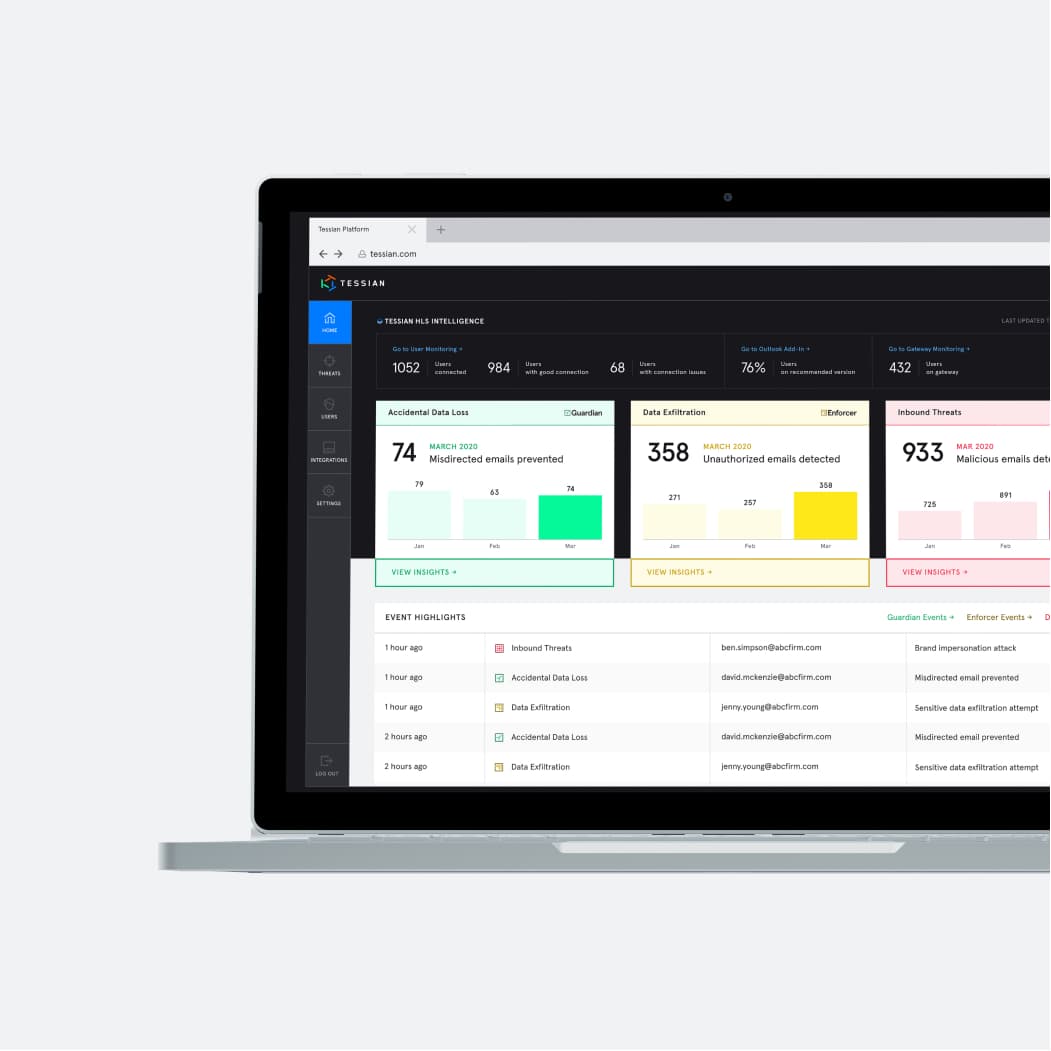
Automatically stop data breaches and security threats caused by employees on email. Powered by machine learning, Tessian detects anomalies in real-time, integrating seamlessly with your email environment within minutes and starting protection in a day. Provides you with unparalleled visibility into human security risks to remediate threats and ensure compliance.